
Types of Rocks Igneous, Sedimentary & Metamorphic » Selftution Metamorphic rocks, Igneous
Rocks are not all the same! The three main types, or classes, of rock are sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous and the differences among them have to do with how they are formed. Sedimentary. Sedimentary rocks are formed from particles of sand, shells, pebbles, and other fragments of material. Together, all these particles are called sediment.
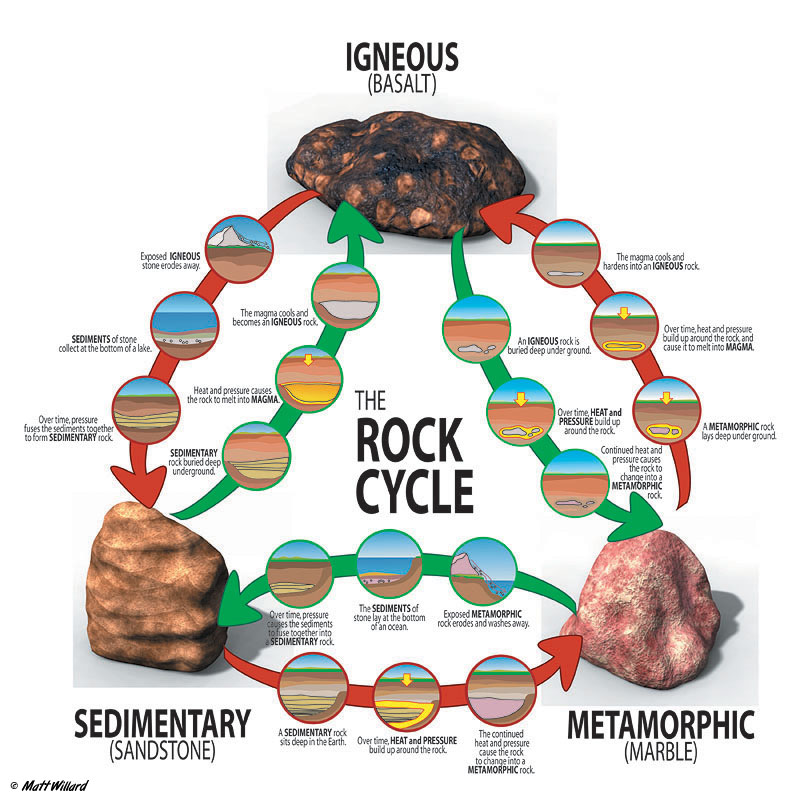
Ms. Thompson's 7th Grade Science Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic Rocks and the Rock Cycle
What are the types of geologic rocks? What are igneous rocks? What are sedimentary rocks? What are metamorphic rocks? What is a rock cycle? rock, in geology, naturally occurring and coherent aggregate of one or more minerals.

Types of Rocks Chart Trend Enterprises
The Three Types of Rocks. Rocks are classified based on how they were formed. The three major types are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. This classification is essential to geologists as it provides critical information about the history of specific regions on Earth. These rocks change forms via the rock cycle.
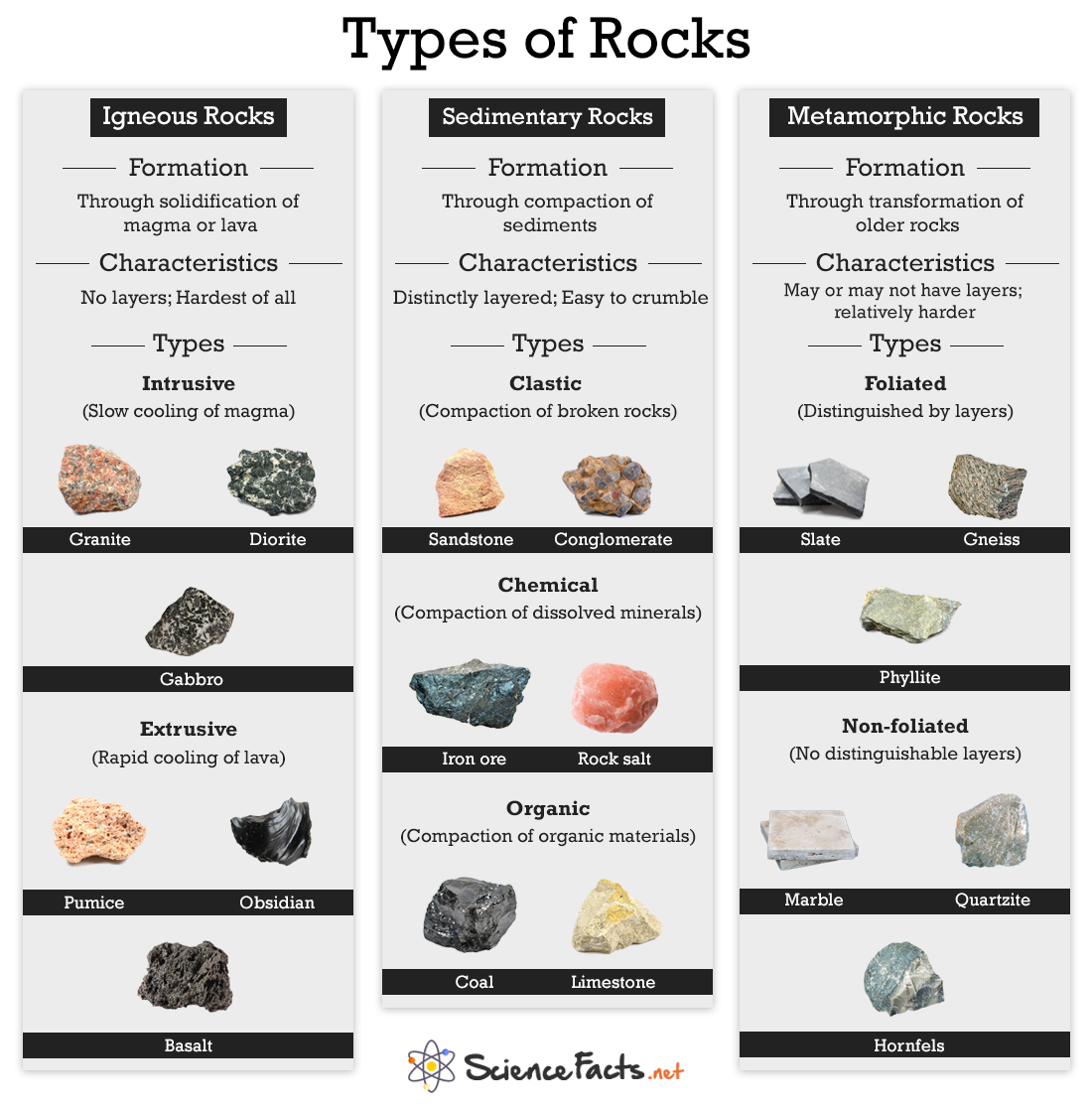
Types of Rocks Science Facts
In short, there are three different types of rocks that every rock you meet can be classified as. The three types of rocks are: Igneous Rocks Metamorphic Rocks Sedimentary Rocks Igneous Rocks The first type of rock on this list are the igneous type of rocks. Igneous rocks are more than just a cool name. They're actually cool in another way.

rock chart Rock and mineral identification Pinterest Charts, Rocks and Poster
Rock Identification Chart Igneous Rock Identification Sedimentary Rock Identification Metamorphic Rock Identification Need More Help? By Andrew Alden Updated on February 24, 2020 Any good rockhound is bound to come across a rock that he or she has trouble identifying, especially if the location of where the rock was found is unknown.

Rocks Classification and Types Construction & Infrastructure
There are three kinds of rock: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks form when molten rock (magma or lava) cools and solidifies. Sedimentary rocks originate when particles settle out of water or air, or by precipitation of minerals from water. They accumulate in layers.

Image result for what type of rock is this rocks Pinterest Best Geology ideas
Dacite Diabase Diorite Gabbro Granite Obsidian Pegmatite Peridotite Pumice Rhyolite Scoria Tuff Unakite Metamorphic Metamorphic Rocks: Photos, descriptions and facts about foliated and non-foliated metamorphic rocks. Amphibolite Anthracite Gneiss Hornfels Lapis Lazuli Marble Mariposite Novaculite Phyllite Quartzite Schist Skarn Slate Soapstone

American Educational Identifying Metamorphic Rock Chart Industrial & Scientific
The classification and description of the various chemically formed sedimentary rock types appears in the bottom section of the chart below. Photos of each rock type appear beneath the chart. Table 5.5.1 5.5. 1: Classification of Sedimentary Rocks. Step 1: Determine makeup.

Geologi, Batuan beku, Geografi
To identify your rock, first take note of its physical properties like color, luster, banding, layering, and grain size. Next, test for hardness and weight by running simple tests. Finally, compare the properties of your rock to those of known rock types while looking for other identifying characteristics. Identifying and classifying rocks can.

Arizona Rock chart Sedimentary, Metamorphic, Basalt, Sandstone, Arizona Rocks, Rock Charts
Figure 4.1.1 4.1. 1: Granite is a classic coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock. The different colors are unique minerals. The black colors are likely two or three different minerals. If magma cools slowly, deep within the crust, the resulting rock is called intrusive or plutonic.
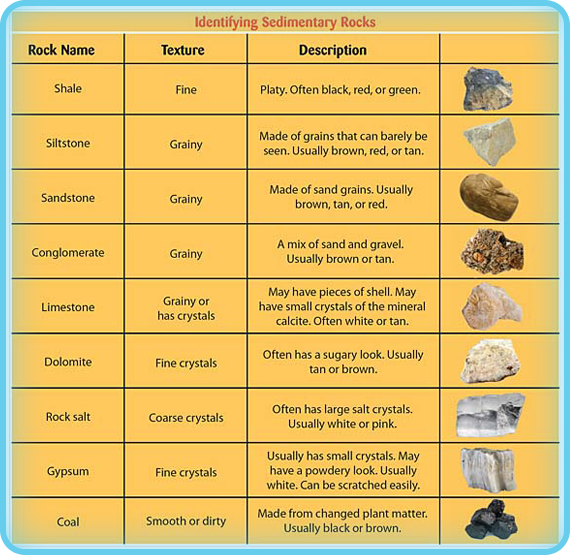
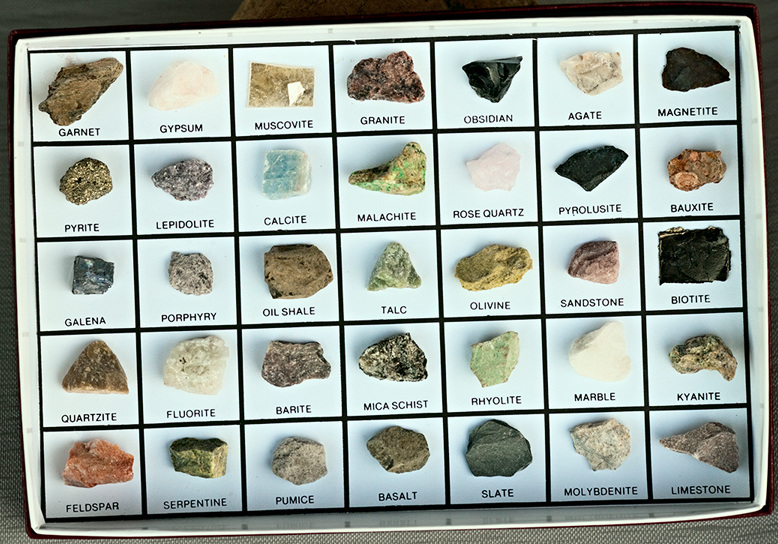
Rocks and minerals images
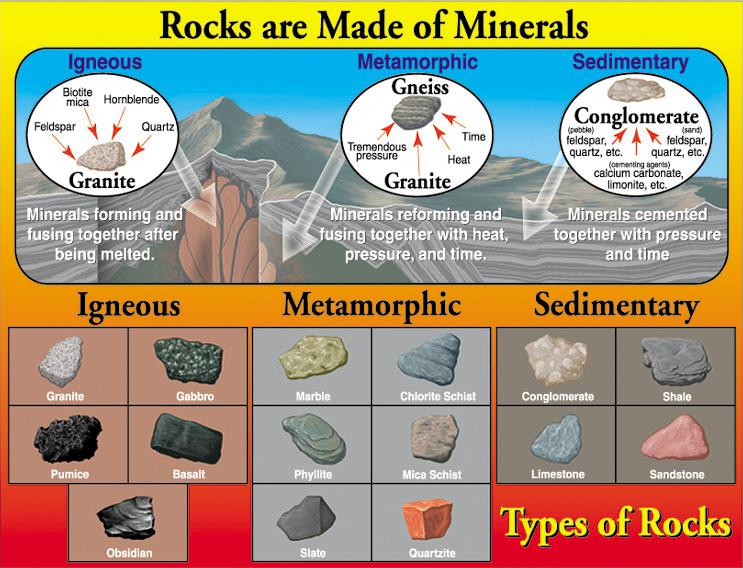
Full color Types of Rocks Chart depicts how rocks are formed from minerals. Five reproducibles on the reverse side of this chart include characteristics and examples of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks, a rock matching game, and a sheet of rock activities. The Types of Rocks Chart measures 43cm x 61cm.

an image of rocks that are labeled in the text, which includes names and pictures
Three Types of Rock Rocks fall into these three groups: Igneous , Sedimentary , and Metamorphic Igneous rocks are formed from melted rock deep inside the Earth. Sedimentary rocks are formed from layers of sand, silt, dead plants, and animal skeletons. Metamorphic rocks formed from other rocks that are changed by heat and pressure underground.
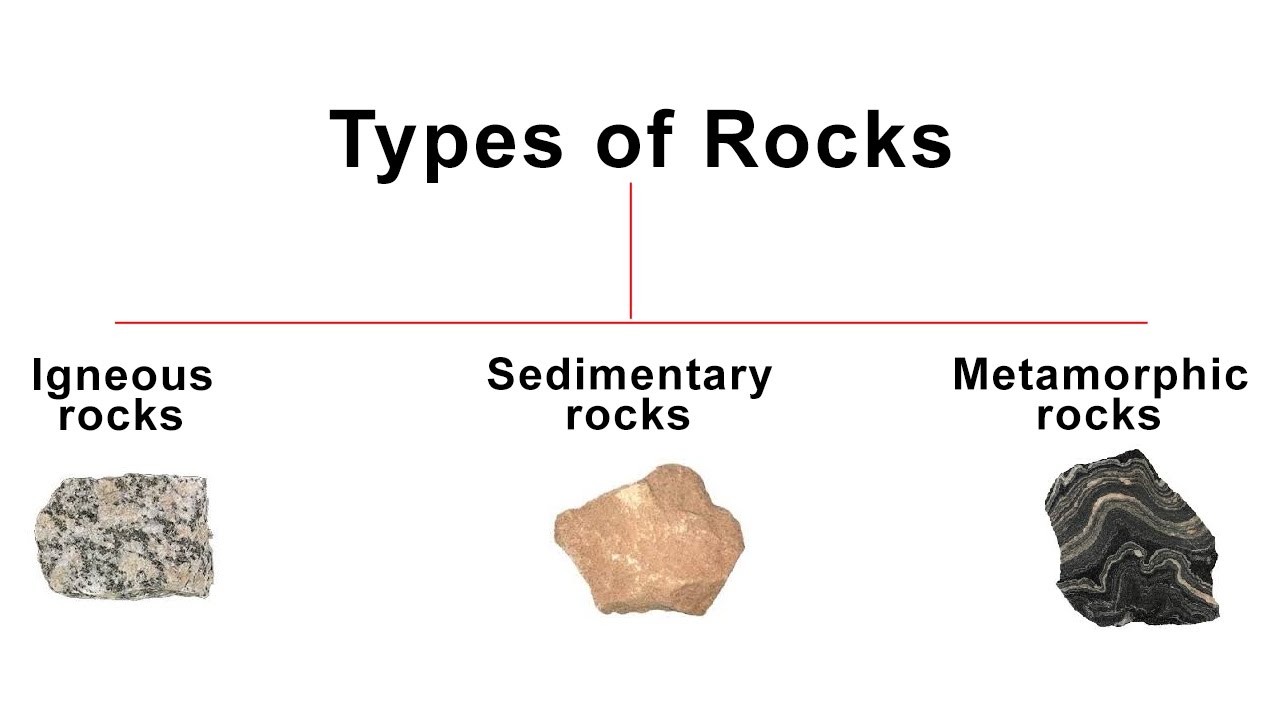
Types of Rocks (2/263/2)
Learn bout igneous rocks such as obsidian, basalt, granite, pumice, rhyolite, and andecite; metamorphic rocks such as marble, slate, gneiss, schist, anthracite, and quartzite; and sedimentary rocks such as sandstone, limestone, conglomerate, shale, travertine, and dolomite. RELATED ACTIVITIES Rocks Scavenger Hunt

Bulletin Board ChartEducationalEarth ScienceTypes of Rock (With images) Rock science, Earth
Types of Igneous Rocks Getty Images By Andrew Alden Updated on June 02, 2019 Igneous rocks are those that form via the process of melting and cooling. If they erupt from volcanoes onto the surface as lava, they are called extrusive rocks. By contrast, Intrusive rocks are formed from magma that cools underground.
Rock Charts Sierra Pelona Rock Club
There are three major types of rock: igneous rock, metamorphic rock, and sedimentary rock. Igneous rocks A sample of andesite (dark groundmass) with amygdaloidal vesicles filled with zeolite. Diameter of view is 8 cm. Adakite - Volcanic rock type Andesite - Type of volcanic rock Alkali feldspar granite - Type of igneous rock rich in alkali feldspar
Rocks and Minerals Information on the earth
Table D: A rough guide to the types of metamorphic rocks that form from different protoliths at different grades of regional metamorphism. You are expected to know the rock names indicated in bold font. Protolith. Very Low Grade (150-300°C) Low Grade (300-450°C) Medium Grade (450-550°C)